In the bag manufacturing business, standing out in a crowded market is just as important as creating great designs and ensuring adherence to ethical standards such as the SMETA audit process. Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit, which evaluates ethical and sustainable manufacturing practices. Industry competition is higher than ever, and your products’ visual appeal and clever marketing aren’t enough to garner success. Retail buyers and shoppers are increasingly invested in the social responsibility of the brands they support. They’ll scrutinize your bags for their construction and materials and proof of your commitment to ethical standards.
If you’re unfamiliar with SMETA, we’ll share everything you need to know below!
Overview of SMETA Auditing
SMETA, or the Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit, is the world’s leading ethical audit methodology for supply chain sustainability. Sedex (Supplier Ethical Data Exchange), an online platform, was developed in 2004 to pioneer ethical and responsible business practices across global supply chains in fashion, electronics, and agriculture.
SMETA: Enhancing Global Labor Conditions and Ethical Business Practices
SMETA is used across 150 countries by over 100,000 facilities to review labor conditions and ethical practices for international standards compliance. The audit supports workers and improves companies by promoting safe working conditions, fair employee treatment, and ethical business practices.
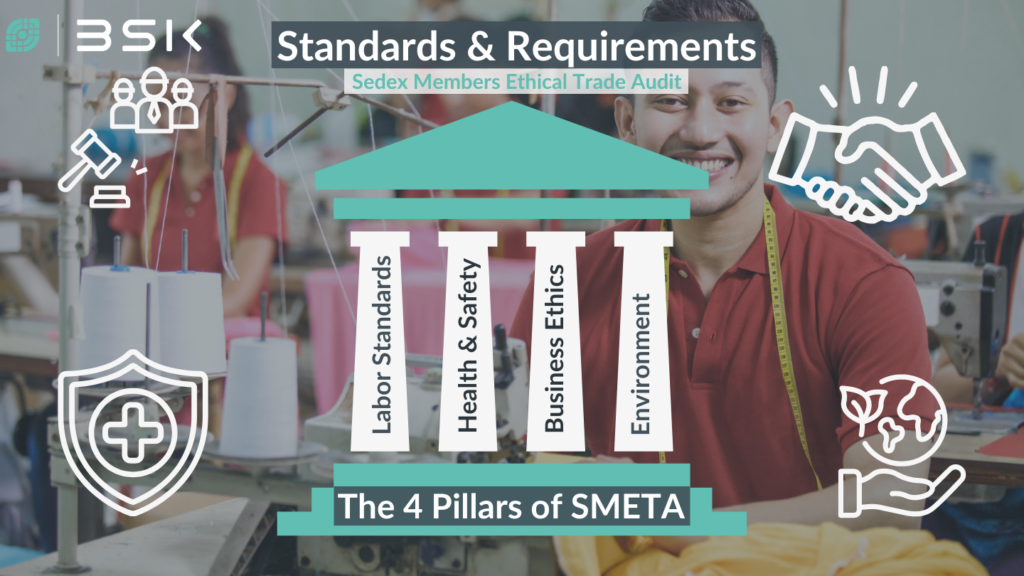
SMETA Standards and Requirements
The SMETA system builds upon four pillars that cover fair labor, sound ethical practices, and environmental safety:
1. Labor Standards
Businesses should comply with international labor laws, ensuring freely chosen employment and prohibiting forced and child labor. Implementing fair wages and working hours gives workers freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining.
2. Health & Safety
Businesses must ensure they provide their workers with a working environment that is safe, hygienic, and healthy. During SMETA audits, experts thoroughly evaluate safety measures businesses have implemented to prevent accidents and injuries. Additionally, these businesses must offer regular health and safety training to their workers, aligning with the best practice guidance from SMETA. Workers should also have access to clean and sanitary facilities, including drinking water, toilets, and areas for food storage, all of which undergo rigorous inspections during SMETA audits. If businesses provide residential housing to employees, they must also ensure these accommodations are clean, safe, and meet the standards SMETA audits scrutinize, securing a comprehensive approach to worker welfare.
3. Environment
Businesses should utilize sustainable operational practices and strive to reduce their environmental impact. Environmental policies should consider energy and water usage, waste disposal, and air emissions. Businesses can create reduction action plans by regularly tracking respective metrics and referring to local and national regulations for guidance.
4. Business Ethics
Businesses should operate in a transparent manner that aligns with legal requirements. Implement effective management systems to ensure the business operates free of bribery or conflicts of interest. All procedures are well-documented, and any relevant certificates, local inspection documents, or permits are available for assessment or review. Consider creating a Business Ethics policy readily available to all employees to promote clear and open communication.
The Benefits and Significance of SMETA Auditing
Taking part in a SMETA audit helps businesses support a sustainable supply chain and positive work environment. The audit protects workers’ rights by ensuring ethical standards throughout the supply chain. Leading to higher workplace satisfaction and retention.
The SMETA auditing system sets manufacturers with other certifications up for success, since it provides a streamlined evaluation process. It helps auditors find areas for improvement and businesses to make corrections and enhance their reputation and operations.
For bag manufacturers, it’s important to demonstrate a commitment to ethical production. This creates stronger trust, helping your business maintain and grow its customer base.

SMETA Auditing Process
SMETA audits are currently only available to Sedex members. You’ll need to book a call with the Sedex team through their website to do so.
Once you join the Sedex platform, you’ll be able to start the audit process, which has several key steps:
1. Application
Receive and complete a pre-audit information pack and a self-assessment questionnaire.
2. Opening Meeting
An auditor from an approved third-party company will arrive on-site and conduct an opening meeting. They will use this time to explain the audit procedure and review necessary documentation. Overviews of management systems/processes, labor contracts, permits/operating licenses, training records, payroll records, and employee handbooks.
3. On-Site Audit
The auditor will conduct a site tour to observe the physical conditions, hold employee interviews, and review necessary records.
4. Closing Meeting
After the site tour, as part of the SMETA audit, a closing meeting will be held to discuss any non-compliances and their root causes. This will initiate the development of the corrective action plan as the auditor and management team discuss potential corrective actions and a suggested implementation timeframe.
5. Audit Report
After the on-site audit, the auditor will send the company an official audit report with a corrective action plan. Depending on the auditing company used, the audit report can arrive just a few days after the on-site audit.
6. Corrective Actions
The business should begin implementing corrective actions within its allotted time frame. They can upload evidence of corrections made to the SEDEX platform. Depending on the case, a follow-up audit may be required.
Businesses are encouraged to undergo regular audits to uphold SMETA standards.
The Industry Relevance of SMETA Auditing
The fashion industry widely recognizes SMETA auditing, and it may even be a requirement to work within certain markets. For instance, the German SCDDA (Due Diligence in the Supply Chain) Act mandates that businesses headquartered in Germany must implement specific ethical obligations that often align with SMETA standards.
SMETA’s ethical and environmental pillars serve as a foundation for any manufacturer looking to display its commitment to transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental regulations. It’s a gateway to higher levels of trust and integrity on all levels of the supply chain.
Alternatives to the SMETA Audit Process
The SMETA Audit is known for its versatility, comprehensive approach, and customizable framework in the realm of ethical and sustainable practices in bag manufacturing. Leveraging the Sedex platform provides a robust tool for benchmarking and improving ethical trade practices. Unlike other certifications, such as the BSCI, SMETA’s strength lies in the adaptability and depth of its audit process. This makes SMETA particularly valuable for companies addressing specific areas of concern within ethical trade and sustainable practices. SMETA’s distinct approach positions it as an essential tool for businesses dedicated to making meaningful improvements in their manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Whether you’re a bag manufacturer seeking a starting point for establishing your commitment to ethics or wanting to give your existing certifications even more credibility, undergoing a SMETA audit is worthwhile. Not only does the exacting audit process help businesses gain a competitive edge in a challenging market, but it also naturally improves operational practices, enhances client confidence, and contributes to a more transparent industry.
